What is Biodiversity?

This post continues from the last one. In that specific lesson, we also learned what biodiversity is. I’ll break down everything.
First of all, what is it? Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth. For example, all plants, all animals, all microorganisms, and the ecosystems they live in. It’s basically different types of every species living.

Levels of Biodiversity
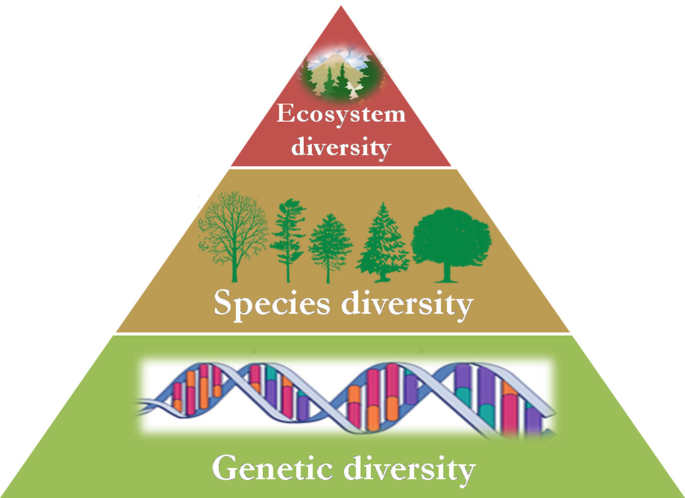
Biodiversity is mostly made up of 3 levels: ecosystem, species, genetic diversity.
Let’s look at each of them. But don’t worry! It’s not gonna be hard to get the idea. Believe me, once you think a little bit logically, you’ll get it.
1. Genetic diversity
This level is about variety inside one species. Every plant, animal, or microorganisms has slightly different genes, and that’s what makes each unique.
For example:
Apples — there are green, red, yellow apples, all are in the same species but different genes. 🍎🍏
Humans — we all are the same species, but we look different. Different shapes, different colors, different length are what makes the genetic diversity.
2. Species diversity
If you understood the first one, this is far easier. This is the number and variety of species living in an area. The more species there are, the richer the biodiversity.
For example:
Fruits – as we mentioned apple genes, apple itself is a species. So, each fruit type (apple, orange, banana, etc.) belongs to a different species.
An area with birds, tigers, elephants, and bears has higher species diversity than an area where there are limited animals.
3. Ecosystem diversity
This is the top level of all ecosystem on Earth, including forests, deserts, oceans, wetlands, farms, etc.
Azerbaijan itself has deserts, forests, mountains, grasslands, and the Caspian Sea — each is a unique ecosystem with its own conditions and species.
Protecting Biodiversity
OK! We got what it is. How about protecting it? According to many resources, biodiversity is decreasing year by year.
We have 2 ways to protect it: in-situ and ex-situ.
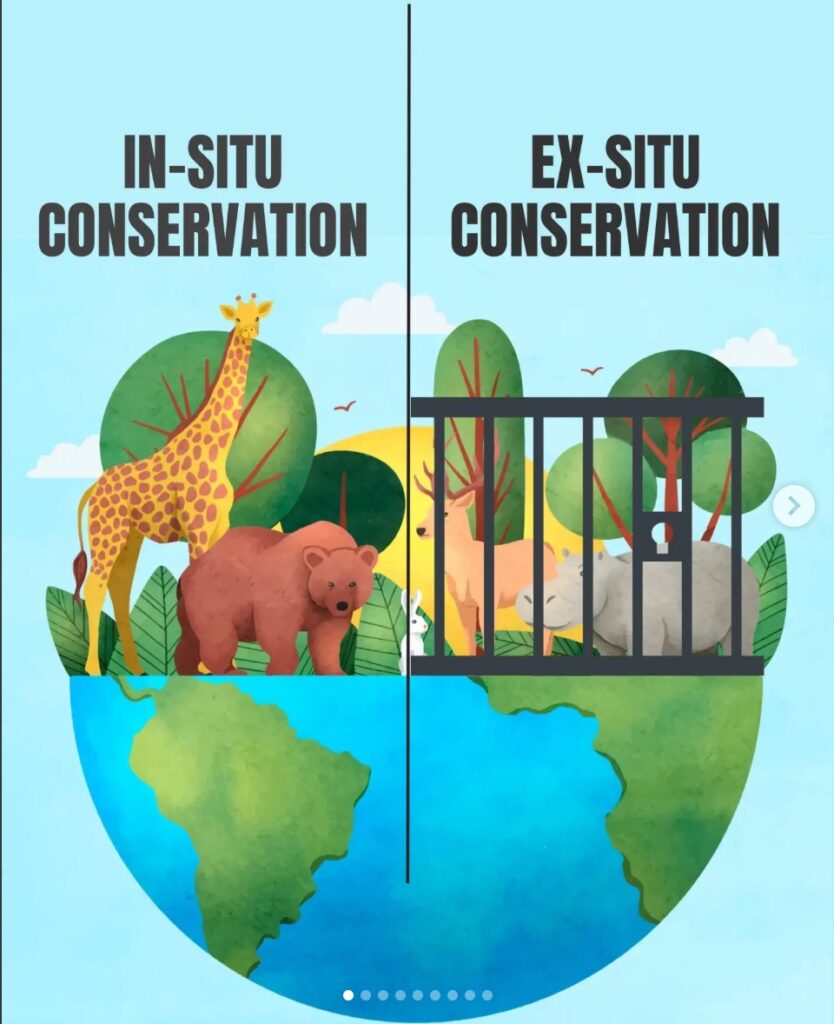

In-situ conservation: This is a way to protect species in their natural homes. That means we save animals and plants where they live. For example, national parks, protected forests, sea services, etc.
Ex-situ conservation: And this is a way, again, to protect species, but outside their natural homes. When animals or plants are too endangered to survive in the wild, we take them to a safe, controlled place to protect and reproduce them. For example, zoos, gardens, aquariums, etc.
How to apply “smart tech” to Biodiversity?
For example, one of the best examples of using tech in biodiversity is the Svalbard Global Seed Vault, located on an island in Norway. It stores more than one million seed samples from over the world. Its goal is to protect plant species from extinction in case of natural disasters, wars, or climate change.
However, it’s not just a storage, rather high-tech, climate-controlled facility. It uses smart sensors and digital monitoring systems to keep the temperature at around -18°C, no matter what happens outside.
End
Yeah. I hope you got the main point, or the whole point. In short, biodiversity means the variety and balance of life on Earth, the foundation of every ecosystem.
Goodbye!