What is Food Security and Safety?

In the 1900s, food security was described with a single definition: “Food Security is an access to sufficient food.” But later this term was changed and replaced with the following:
Food security is achieved when all people, at all times, have access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs for a healthy life.
Yes, as you can see, this term is simply an expanded version of the previous one. With a closer look, we can understand that it’s not just about having enough food, but also about having nutritious and safe food.
Each of these definitions was written by the FAO — the World Food Conference. The first in 1974, the second in 1996.
Pillars of Food Security
Food security (FS) consists of 4 parts. Each of them has its own role. These include the features mentioned in the definition above:
- Availability
- Access
- Stability
- Utilization

Availability
Food availability consists of several criteria, such as:
Domestic production – producing enough food within the country to meet people’s needs.
Import capacity – having the ability to buy food from abroad when domestic production is insufficient.
Food stocks – stored food kept by governments or markets for shortages or emergencies (in simple words, “backup food”).
Food aid – food support for people who cannot afford enough food. This can come from the government, international organizations, or humanitarian groups.
Access
Access to food is basically measured with 2 criteria:
Purchasing power – people’s financial ability to buy nutritious and healthy food.
Market infrastructure – systems that enable efficient distribution of food products from producers to consumers.
Stability
Food stability includes several factors:
Weather variability – I wrote about climate change in my previous blog. This is exactly related. Warming, fluctuations, and other climate issues affect crops.
Price changes – rapid changes in food prices.
Political factors – government policies that affect food availability and distribution.
Utilization
Finally, we have food utilization.
This first considers food quality and diversity. As the name suggests: higher-quality and more diverse food.
Interestingly, food safety is actually part of food utilization.
What is Food Safety?

Food safety means the absence of contaminants and toxins in food that make it dangerous. In other words, protecting people from foodborne illnesses. This includes the processes used during harvesting, preparation, storage, and distribution.
Food contamination usually comes from physical, chemical, biological, or microbiological sources.
Examples for each:
- Objects that may enter food during processing or delivery (physical),
- small cleaning tools (physical),
- detergent (chemical),
- pesticides (chemical),
- insects that can contaminate food (biological),
- bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can transfer during food handling (microbiological).
How Food Safety Affects Food Security
When food safety is properly managed, food loss decreases, and food availability, stability, and utilization increase. It also improves nutrition and public health.
Main Factors Affecting Food Security
Population growth: The global population is increasing rapidly, and it is expected to reach around 9.7 billion by 2050.
Today, around 783 million people face hunger. Research shows that by 2030, about 600 million people will struggle to feed their families.
Vitamin A, iron, and iodine deficiencies are the top 3 global nutritional deficiencies.
Climate change: Climate change and extreme phenomena such as drought, floods and heat waves can destroy crops and, thereby increase the risk of food insecurity. You can read more about this in this blog.
Price increases: Price volatility can create major weaknesses in a country’s food security.
Up to this point, we’ve learned what food security and safety mean. Now we can end with an interesting fact.
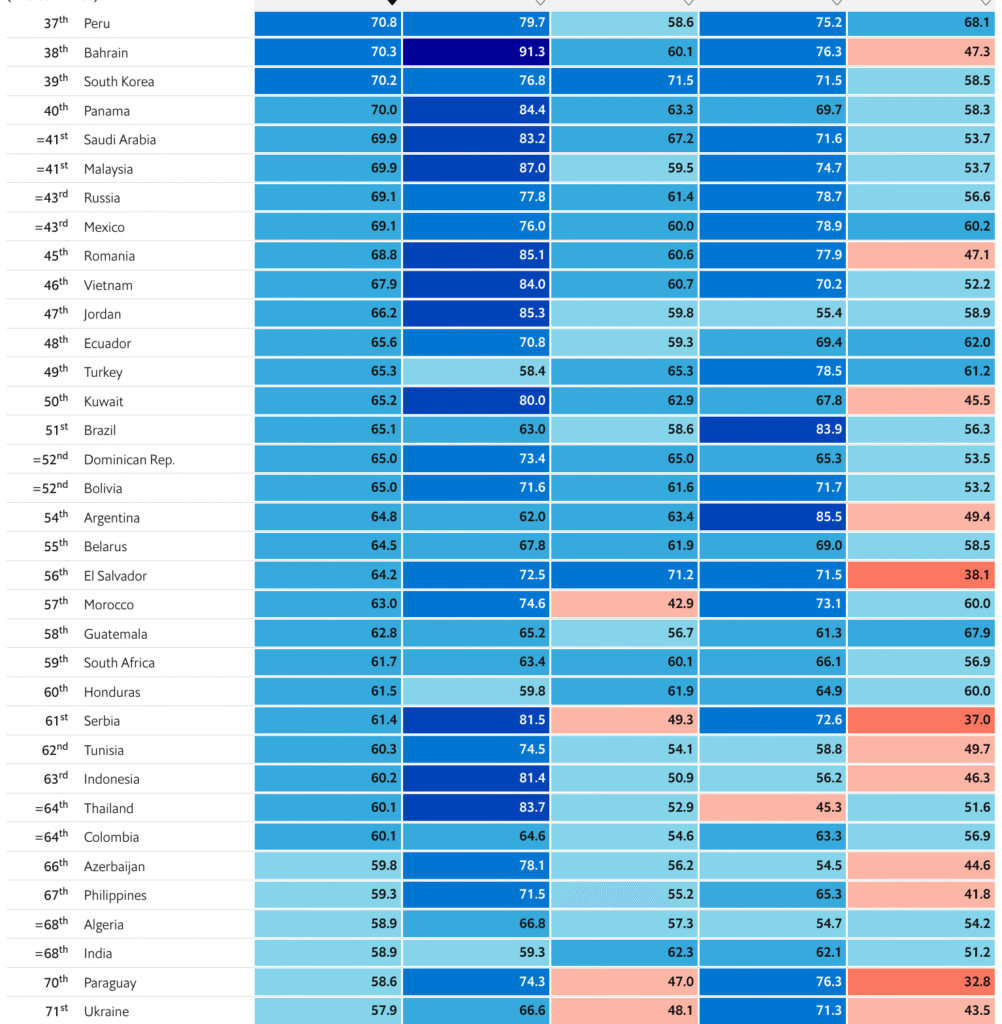
Index Scores for the Global Food Security Index (2022)
The GFSI — the Global Food Security Index — evaluated countries in 2022 and basically gave each one an exam score measuring their food security performance.
Azerbaijan ranked 66th. Turkey ranked 49th, and Russia ranked 43rd.
Finland ranked first.
Conclusion
In the end, we can say food security is needed in agriculture. And food safety is a sub-layer of security.
Food Security – ensuring access to sufficient nutritious food by securing its availability, accessibility, stability, and utilization.
Food Safety – protecting food from contamination through hygiene, proper handling, preparation, and storage, thereby preventing foodborne illnesses.